线程状态
目录
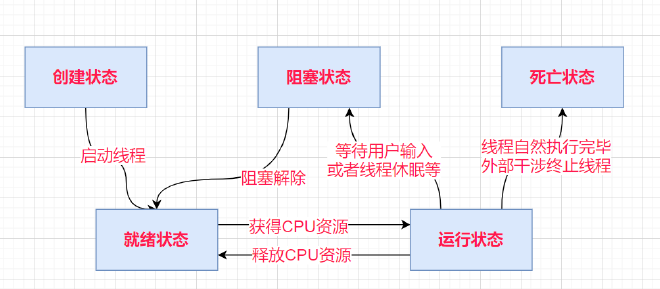
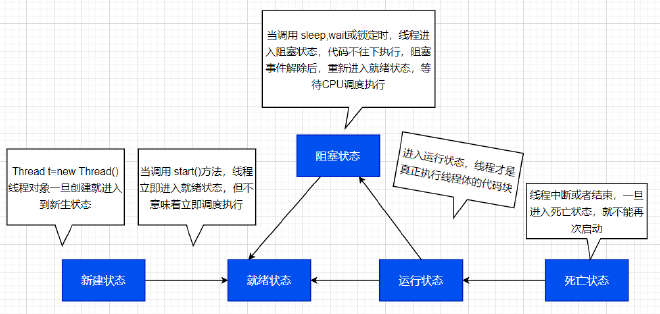
线程五状态 #
线程方法 #
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| setPriority(int newPriority) | 更改线程的优先级 |
| static void sleep(long mills) | 在指定毫秒内让当前正在执行的线程休眠 |
| void join() | 等待该线程终止 |
| static void yield() | 暂停当前正在执行的线程对象,并执行其他线程 |
| void interrupt() | 中断线程,不太推荐使用的方法 |
| boolean isAlive() | 测试线程是否处于活动状态 |
停止线程(stop)已弃用 #

/**
* 测试stop
* 1.建议线程正常停止-->利用次数,不建议死循环
* 2.建议使用标志位-->设置一个标志位
* 3.不要使用stop或者destroy等过时或者JDK不建议使用的方法
*/
public class Demo15_StopThread implements Runnable {
// 1. 设置一个标志位
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while (flag) {
System.out.println("run...Thread" + i++);
}
}
// 2. 设置一个公开的方法停止线程,转换标志位
public void stop() {
this.flag = false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo15_StopThread stop = new Demo15_StopThread();
new Thread(stop).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("main..." + i);
if (i == 900) {
//调用stop()切换标志位,让线程终止
stop.stop();
System.out.println("该线程停止了");
}
}
}
}
线程休眠(sleep) #

/**
* 模拟网络延迟:放大问题的发生性
*/
public class Demo16_SleepThread implements Runnable {
//票数
private int ticketNums = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
if (ticketNums <= 0) {
break;
}
//捕获异常
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->拿到了第" + ticketNums-- + "张票");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo4_TrainTicketsCase ticket = new Demo4_TrainTicketsCase();
new Thread(ticket, "小红").start();
new Thread(ticket, "老师").start();
new Thread(ticket, "黄牛1").start();
}
}
/**
* 模拟倒计时
*/
public class Demo17_SleepThread2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
tenDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//模拟倒计时
public static void tenDown() throws InterruptedException {
int num = 10;//10秒
while (true) {
//相当于延时1000毫秒
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(num--);
if (num <= 0) {
break;
}
}
}
}
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* 每一秒获取当前时间
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取系统当前时间
LocalDateTime startTime;
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
//更新系统时间
System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now().getSecond());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
线程礼让(yield) #
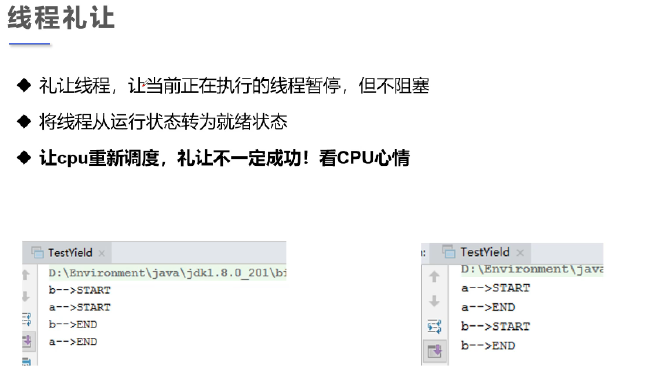
/**
* 测试礼让线程
* 礼让不一定成功,看cpu心情
*/
public class Demo19_YieldThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyYeild myYeild = new MyYeild();
new Thread(myYeild, "a").start();
new Thread(myYeild, "b").start();
}
}
class MyYeild implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程开始执行");
Thread.yield();//礼让
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程停止执行");
}
}
线程插队(join) #
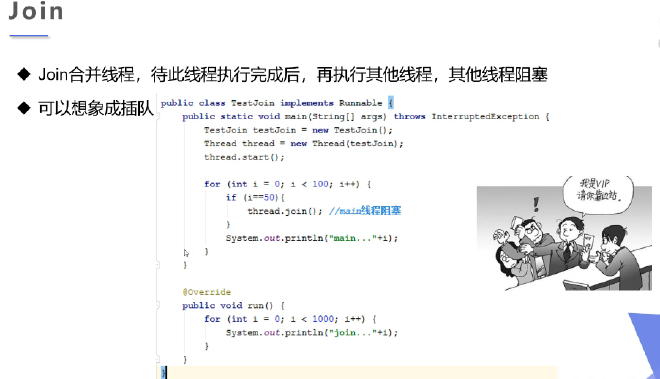
/**
* 测试join
* 插队
*/
public class Demo20_JoinThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
System.out.println("线程vip" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//启动我们的线程
Demo20_JoinThread joinThread = new Demo20_JoinThread();
Thread thread = new Thread(joinThread);
thread.start();
//主线程
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
if (i == 200) {
thread.join();//插队
}
System.out.println("main" + i);
}
}
}
/*
main196
main197
main198
main199
线程vip0
线程vip1
线程vip2
*/
线程状态观测(Thread.State) #

/**
* 观察测试线程状态
*/
public class Demo21_ThreadState {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("//");
});
//观察状态
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
//观察启动后
thread.start();
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);//Run
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED) {//只要现成不终止,就一直输出状态
Thread.sleep(100);
state = thread.getState();//更新线程状态
System.out.println(state);
}
//死亡后的线程不能再启动了,启动会报异常
//thread.start();
}
}
线程的优先级(PRIORITY) #

/**
* 线程优先级
*/
public class Demo22_ThreadPriority{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//主线程默认优先级
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
MyPriority myPriority = new MyPriority();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread thread4 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread thread5 = new Thread(myPriority);
//先设置优先级,再启动
thread1.start();
thread2.setPriority(1);
thread2.start();
thread3.setPriority(4);
thread3.start();
thread4.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);//MAX_PRIORITY=10
thread4.start();
thread5.setPriority(8);
thread5.start();
}
}
class MyPriority implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
}
/*
main-->5
Thread-3-->10
Thread-4-->8
Thread-0-->5
Thread-2-->4
Thread-1-->1
*/
守护线程(Daemon) #
- 线程分为用户线程和守护线程
- 虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕(比如主线程)
- 虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕
- 守护线程的作用比如:后台记录操作日志,监控内存,垃圾回收等待…..

/**
* 测试守护线程
* 上帝守护你
*/
public class Demo23_DaemonThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
God god = new God();
You you = new You();
Thread thread = new Thread(god);
//默认false表示是用户线程,正常的线程都是用户线程...
thread.setDaemon(true);
//上帝守护线程启动
thread.start();
//你 用户线程启动
new Thread(you).start();
}
}
//上帝
class God implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("上帝保佑着你");
}
}
}
//你
class You implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 36500; i++) {
System.out.println("你一生都开心的活着");
}java
System.out.println("====goodbye!world====");
}
}
wait和sleep的区别 #
- 来自不同的类:wait => Object ;sleep => Thread
一般情况企业中使用休眠是:
TimeUnit.DAYS.sleep(1); //休眠1天
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); //休眠1s
- 关于锁的释放:wait 会释放锁 ;sleep睡觉了,不会释放锁
- 使用的范围是不同的:wait 必须在同步代码块中;sleep 可以在任何地方睡
- 是否需要捕获异常:wait是可以不用捕获异常;sleep必须要捕获异常